BGP Questions
|
BGP Quick Summary: Protocol type: Path Vector |
| More information about popular Path Selection Attributes |
|
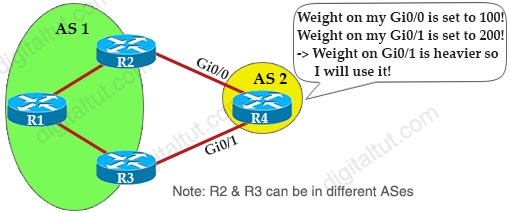
Weight Attribute: This is an example of configuring Weight attribute: -> R4 will choose R3 to forward packets. |
|
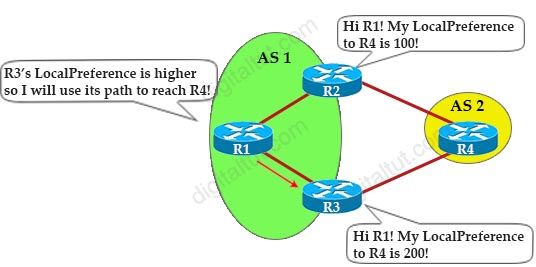
Local Preference (LocalPrf) Attribute:
Note: Although Local Preference attribute is only sent to all iBGP neighbor and it is not exchanged between eBGP neighbors but we can apply it to an eBGP neighbor (inbound direction) to affect our local AS choice. For example in the topology above, we can use Local Preference on R2 (inbound direction) for the R2-R4 eBGP connection (command like “neighbor 192.168.24.4 route-map LOCAL-PREF-150 in”) to affect routing decision on R1 toward R4. Unlike Weight attribute, Local Preference attribute is advertised to all iBGP neighbors. |
|
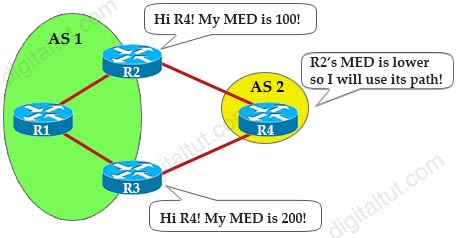
MED Attribute:
|
|
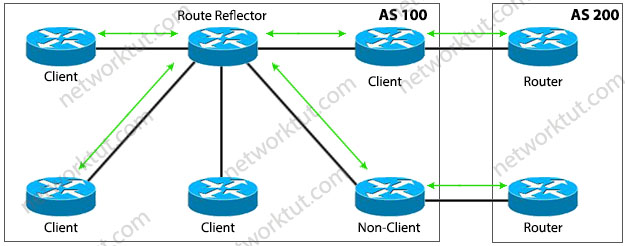
Route Reflector (RR) IBGP routers do not re-advertise routes learned via IBGP to other IBGP peers. One of the two solutions for this is configuring a Route Reflector. A BGP route reflector is an IBGP speaker that reflects or repeats routes learned from IBGP peers to some of its other IBGP peers.
The route reflector can have three type of peerings: When a route reflector forwards a route, there are a couple of rules: All configuration of the route reflector is done on the RR itself. The configuration that identifies which IBGP peers are RR clients (or non-clients) is done from the RR only. To avoid a single point of failure, redundant route reflectors are typically used. |
Question 1
Explanation
With route reflector (RR), we only need to establish a BGP session from the RR to each internal peer -> Answer A is not correct.
We can advertise both classful and classless prefix to other clients, provided that the prefix satisfies the RR forwarding rules -> Answer B and answer C are not correct.
Therefore only answer D is left. Maybe we are missing an IGP in our topology so R2 did not know how to reach the next hop reported by the prefix.
Question 2
Explanation
The “conform-action” specifies the action to take on packets that conform to the rate limit and the “exceed-action” specifies the action to be taken on packets when the packet rate is greater than the rate specified in the maximum-burst-bytes argument.
Question 3
Explanation
From the configuration above, we learn that the local-preference and weight in BGP updates received from neighbor 10.222.1.1 are updated to 250 and 200, respectively (provided that it matches the AS-PATH in ACL 200).
To answer this question, we have to clearly understand the difference between local-preference and weight attribute. The local-preference attribute is used to influence the routing decision on the neighbor IBGP router while the weight attribute is used to influence the routing decision on the local router (as it is only used locally in a router). Therefore in this case we have to use the weight attribute -> Answer D is correct.
Question 4
Explanation
The “show policy-map control-plane” is used to display the service-policy associated to the control-plane. It also shows the packets that matched the class-map. In the output above, we see the line “Match: access-group name BGP” and the next line “drop” in the first class-map BGP which mean “all traffic matched by ACL BGP is dropped”.
Note: “match-all” means “all conditions have to match for the match to occur”. For example:
class-map match-all BGP
match access-group 10
match access-group 20
-> Must match both ACL 10 and ACL 20.
Question 5
Explanation
Idle (PfxCt) means the session is in the Idle state because the neighbor has sent more prefixes than the configured maximum-prefixes limit.
| router bgp 100 neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 200 neighbor 10.0.0.1 maximum-prefix 10 80 |
In the last command, “10” is the maximum number of prefixes allowed from the neighbor and the router starts to generate a warning message at 80%.
Therefore if the BGP neighbor sent 11 prefixes, the local router will be in Idle (PfxCt) state.



what is the answer for Q3
@TT C
cannot see questions.. why? someone please reply
If anyone is curious, this is the exhibit for Q3. Anyone know the answer- this one is tough!
https://www.examtopics.com/discussions/cisco/view/25647-exam-300-410-topic-1-question-24-discussion/
I believe the answer to Question 3 (A. The local preference value in another neighbor statement is higher than 250) is incorrect.
The explanation given states “The local-preference attribute is used to influence the routing decision on the local router while the weight attribute is used to influence the routing decision on the neighbor router.”
However, according to Cisco documentation, Weight is locally significant to the router and is not propagated or carried through any of the route updates. Local Preference is propagated to intra-AS neighbors only. Weight takes precedence over Local Preference in the BGP Path Selection process. Thus, the Answer should be D. The weight value in another statement is higher than 200
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/border-gateway-protocol-bgp/13753-25.html
@EnterNameHere: Thanks for your detection. We have just updated Q.3.
Why is Q2 D?
Policy Map COPP
Class BGP
police cir 1000k bc 1500
conform-action transmit
exceed-action drop – Doesnt the drop here, drop traffic instead of ignoring it?
I agree with Tin. “IGNORE” is the same as “DROP”???
What is DevNetwork
It says refer to the exibit but I don’t see an exibit.
…
Q3
A. The local preference value in another neighbor statement is higher than 250
B. The local preference value should be set to the same value as the weight in the route map
C. The route map is applied in the wrong direction
D. The weight value in another statement is higher than 200
Answer: D Or C?
Please confirm